Explanation:
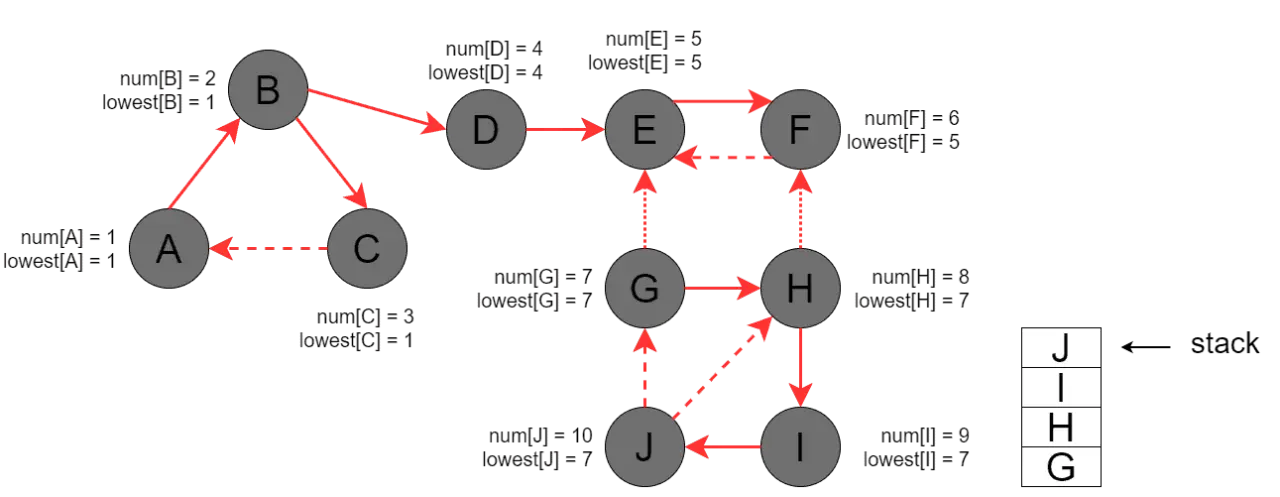
maintain two arrays: Tin[] and low[] tin stores the time taken by dfs to reach the ith node from source. low stores the minimum time taken by dfs to reach the ith node from source.
class Solution {
public:
int timer=1;
void dfs(int node, int parent, vector<int>&tin, vector<int>&vis, vector<int>&low, vector<vector<int>>&graph, vector<vector<int>>&bridges){
vis[node]=1;
tin[node] = low[node] = timer;
timer++;
for(auto it: graph[node]){
if(it==parent)continue;
if(vis[it]==0){
dfs(it, node, tin, vis, low, graph, bridges);
low[node] = min(low[node], low[it]);
if(low[it]>tin[node]){
bridges.push_back({node, it});
}
}
else{
low[node] = min(low[node], low[it]);
}
}
}
vector<vector<int>> criticalConnections(int n, vector<vector<int>>& connections) {
vector<vector<int>>graph(n);
for(auto it: connections){
graph[it[0]].push_back(it[1]);
graph[it[1]].push_back(it[0]);
}
vector<int>vis(n+1, 0);
vector<int>tin(n);
vector<int>low(n);
vector<vector<int>>bridges;
dfs(0, -1, tin, vis, low, graph, bridges);
return bridges;
}
};